
 |
Purpose
Classifications provide the options that a User can select for specific predefined Classification Types.
“Classifications” is the generic description used for this grouping mechanism.
One or more pre-configured Classification can be configured for the following Classification Types.
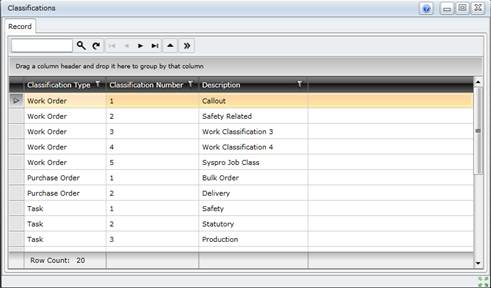
1. Click Shared Configuration - Classifications then ![]() Browse.
Browse.
The Classifications browse window opens.
Business rules
Please note!
How Classifications are used
This table describes how Classifications are used.
|
Classification Type |
Classifications on… |
Are used to… |
|
Work Order Classifications (1 to 5) |
User - Work tab |
Specify default Work Order Classification Allowed Values to use when adding a (scheduled or unplanned) Work Order. |
|
Work Order - Work Order Classifications tab |
Group Work Orders for reports and profiles. Defaults to the Work Order Classification Allowed Values specified for the User who added an unplanned Work Order, or created scheduled Work Orders from Proposed Work Orders. |
|
|
Task
|
User -Tasks tab |
Specify the default Task Classification Allowed Values to use when adding Tasks for Proposed Work Order if defaults were not specified for the Asset Task or Standard Task. |
|
Asset Task - Classifications tab |
Specify the default Task Classification Allowed Values to use for the Task when adding a Work Order for the Asset or generating Proposed Work Orders for scheduled work, if applicable. |
|
|
Proposed Work Orders - Filter, Split and Combination Options |
Specify the Task Classifications that result in separate Work Orders being generated for Tasks with different Allowed Values. |
|
|
Work Order - Tasks Classifications tab
|
Show the Classification Allowed Values that apply to all the Work Order’s Tasks if Classification Allowed Values are not specified for the Asset Task or User. |
|
|
Work Order, Tasks for Work Order |
Show the Classification Allowed Values that apply to the Work Order’s Task. Classification Allowed Values are populated from:
|
|
|
Task Feedback Classifications (1 to 5) |
Work Order, Tasks for Work Order |
Provide a standard way of classifying Work Order feedback. Task Feedback Classifications with specific allowed values can be used to analyse the Tasks that are executed for a Work Order. |
|
Purchase Order Classifications (1 to 2) |
Purchase Order -Classifications tab |
Group Purchase Orders for reports and profiles. |
|
Work Order Classifications Management in a factory environment need to distinguish between urgent Work Orders that are raised and must be completed during normal operating hours, and Work Orders that are raised after hours by engineering staff who are called out by the night-shift to work overtime. Classifications provide an alternative to setting up different Types of Work, and allow analysis of Work Orders at multiple levels. These Allowed Values could apply to a Work Order Classification “Callout”.
Task Classifications Task Classifications are used by Proposed Work Orders to group Asset Tasks for scheduled Work Orders. If Tasks with different values for “Safety” will be generated on separate Work Orders is selected as a criterion on the Generate Proposed Work Orders window then a proposed Work Order for an Asset is generated for each group of Asset Tasks with a matching Classification andAllowed Value. All Tasks for each proposed Work Order have the same “Safety” Classification, and Tasks with different “Safety” Classifications appear on different scheduled Work Orders. As a result,
Task Feedback Classifications Task Feedback Classifications provide Planners with a standard way of classifying Work Order feedback. Classifications with specific allowed values can be used to analyse the Tasks that are completed for Work Orders. For example, possible Allowed Values for Classification “Condition of replaced part” are “Still Good”, “Normal Expected Wear” and “Close to Failure”. After a period of time a Work Order Task (e.g. Replace Bearing) can be analysed by Classification to check the accuracy of the task’s scheduling frequency. Task Feedback Classifications could also be used to record the name of the technician who performed the Task.
|